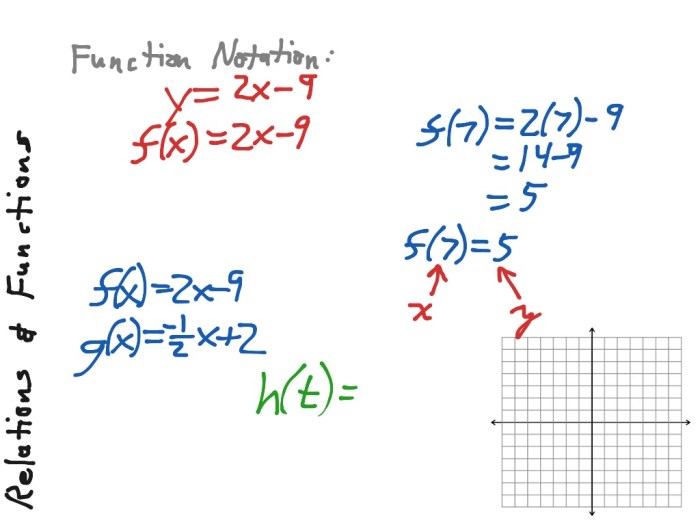Unit 2 linear functions homework 1 relations and functions – Unit 2 Linear Functions Homework 1: Relations and Functions introduces the fundamental concepts of linear functions and relations. This homework delves into the properties and characteristics of these mathematical entities, providing a solid foundation for further exploration in mathematics.
Through a comprehensive table comparing relations and functions, students gain a clear understanding of their distinct features. A concise blockquote summarizes the key takeaways, reinforcing the essential concepts covered. The homework emphasizes the significance of understanding relations and functions, highlighting their pervasive role in various mathematical applications.
Unit 2: Linear Functions
Linear functions represent a fundamental concept in mathematics. They are characterized by a constant rate of change, known as the slope, and a vertical intercept, referred to as the y-intercept. The equation of a linear function is typically written in the form y = mx + b, where ‘m’ represents the slope and ‘b’ represents the y-intercept.
Linear functions exhibit a wide range of applications in various fields. For instance, they are commonly used to model linear relationships between two variables, such as the relationship between the distance traveled and the time taken. Understanding linear functions is crucial for analyzing and interpreting data, making predictions, and solving real-world problems.
Examples of Linear Functions, Unit 2 linear functions homework 1 relations and functions
- y = 2x + 3 (slope = 2, y-intercept = 3)
- y = -x + 5 (slope = -1, y-intercept = 5)
- y = 3 (slope = 0, y-intercept = 3)
Graphing Linear Functions
Linear functions can be easily graphed using the slope-intercept form (y = mx + b). The slope determines the steepness and direction of the line, while the y-intercept indicates the point where the line crosses the y-axis. By plotting the y-intercept and using the slope to find additional points, the graph of a linear function can be constructed.
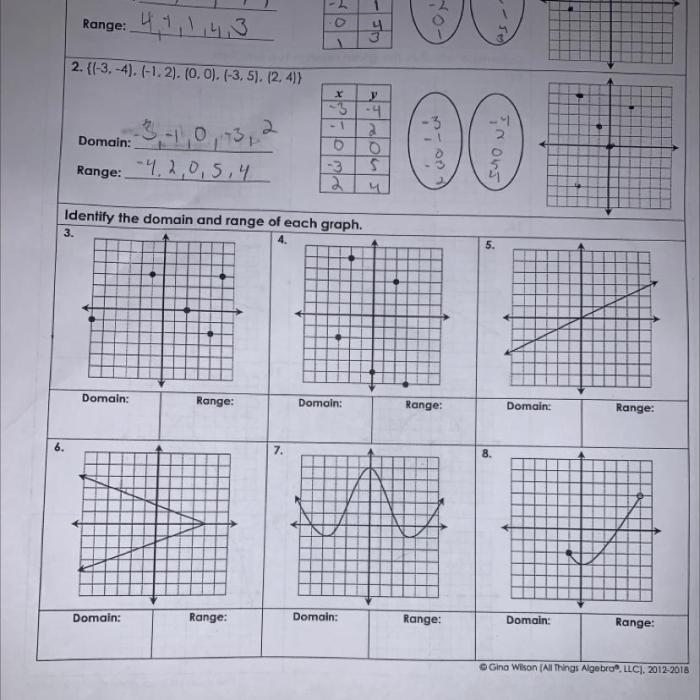
Relations and Functions
Relations and functions are two closely related concepts in mathematics. A relation is a set of ordered pairs, while a function is a special type of relation that satisfies the property of one-to-one correspondence.
Properties of Functions
- Domain:The set of all possible input values for the function.
- Range:The set of all possible output values for the function.
- One-to-One Correspondence:For each input value, there is only one corresponding output value.
Examples of Relations that are not Functions
- (1, 2), (2, 1), (3, 2)
- (x, y) | y = x^2
Homework 1: Relations and Functions: Unit 2 Linear Functions Homework 1 Relations And Functions
| Karakteristik | Relasi | Fungsi |
|---|---|---|
| Definisi | Himpunan pasangan berurutan | Relasi dengan sifat korespondensi satu-satu |
| Domain | Himpunan nilai input | Himpunan nilai input yang unik |
| Range | Himpunan nilai output | Himpunan nilai output yang unik |
| Contoh | (1, 2), (2, 1), (3, 2) | (1, 2), (2, 3), (3, 4) |
Konsep Kunci:
- Linear functions memiliki persamaan y = mx + b, di mana ‘m’ adalah kemiringan dan ‘b’ adalah titik potong y.
- Relasi adalah himpunan pasangan berurutan, sedangkan fungsi adalah relasi dengan sifat korespondensi satu-satu.
- Domain dan range adalah himpunan nilai input dan output dari suatu fungsi.
Memahami relasi dan fungsi sangat penting dalam matematika. Fungsi digunakan secara luas untuk memodelkan hubungan antara variabel dan untuk membuat prediksi. Memahami konsep-konsep ini sangat penting untuk kesuksesan dalam matematika dan bidang terkait.
FAQ Insights
What is the difference between a relation and a function?
A relation is a set of ordered pairs, while a function is a relation where each input value corresponds to exactly one output value.
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear function?
The slope-intercept form of a linear function is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
What is the domain of a function?
The domain of a function is the set of all possible input values.