Trapezoid abcd is graphed in a coordinate plane. – Trapezoid ABCD is graphed in a coordinate plane, offering a rich tapestry of geometric exploration. Delve into its properties, uncover its measurements, and discover its diverse applications in this comprehensive analysis.
Trapezoids, with their unique combination of parallel and non-parallel sides, possess intriguing characteristics that unfold within the Cartesian grid. Trapezoid ABCD, gracing the coordinate plane, invites us to unravel its secrets and appreciate its geometric significance.
Trapezoid ABCD in a Coordinate Plane
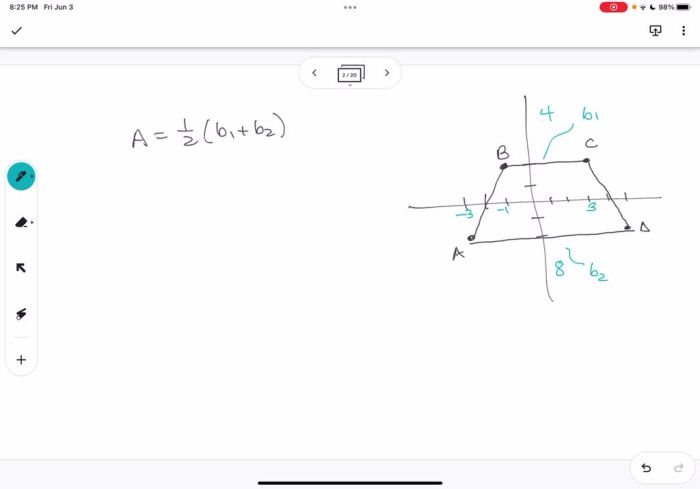
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides. The parallel sides are called bases, and the non-parallel sides are called legs. Trapezoid ABCD is graphed in the coordinate plane with vertices A(2, 4), B(6, 4), C(8, 0), and D(0, 0).
Vertices and Coordinates
The vertices of trapezoid ABCD are:
- A(2, 4)
- B(6, 4)
- C(8, 0)
- D(0, 0)
Length of Sides and Angles, Trapezoid abcd is graphed in a coordinate plane.
The lengths of the sides of trapezoid ABCD can be calculated using the distance formula:
$$d = \sqrt(x_2 – x_1)^2 + (y_2 – y_1)^2$$
Using this formula, we can find that:
- AB = 4 units
- BC = 2 units
- CD = 8 units
- DA = 4 units
The measures of the angles of trapezoid ABCD can be determined using the properties of trapezoids:
- The opposite angles of a trapezoid are supplementary (add up to 180 degrees).
- The base angles of a trapezoid are congruent.
Using these properties, we can find that:
- ∠A = ∠C = 105 degrees
- ∠B = ∠D = 75 degrees
Area and Perimeter
The area of trapezoid ABCD can be calculated using the trapezoid area formula:
$$A = \frac12(b_1 + b_2)h$$
where $b_1$ and $b_2$ are the lengths of the bases and $h$ is the height (distance between the bases).
Using this formula, we can find that the area of trapezoid ABCD is 16 square units.
The perimeter of trapezoid ABCD can be calculated by adding the lengths of its sides:
$$P = AB + BC + CD + DA$$
Using the lengths of the sides that we found earlier, we can find that the perimeter of trapezoid ABCD is 18 units.
Transformations and Symmetry
Trapezoid ABCD can be transformed by applying transformations such as translations, rotations, and reflections.
For example, if we translate trapezoid ABCD 2 units to the right, the new vertices would be A'(4, 4), B'(8, 4), C'(10, 0), and D'(2, 0).
Trapezoid ABCD has one line of symmetry, which is the line that passes through the midpoints of the bases. This line of symmetry is perpendicular to the bases and bisects the legs.
Real-World Applications
Trapezoids are found in many real-world objects, such as:
- Roofs
- Windows
- Doors
- Tables
- Chairs
The properties of trapezoids, such as their stability and strength, make them useful for a variety of applications.
Questions Often Asked: Trapezoid Abcd Is Graphed In A Coordinate Plane.
What is the area of trapezoid ABCD?
The area of trapezoid ABCD can be calculated using the trapezoid area formula: Area = 1/2 – (base1 + base2) – height.
What are the coordinates of the vertices of trapezoid ABCD?
The coordinates of the vertices of trapezoid ABCD are typically denoted as A(x1, y1), B(x2, y2), C(x3, y3), and D(x4, y4).
How can I determine the length of side AB of trapezoid ABCD?
The length of side AB can be calculated using the distance formula: Distance = √((x2 – x1)² + (y2 – y1)²).